Enhancing Business and Individual Planning with SOSTAC Analysis
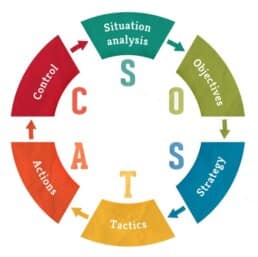
Introduction In a world driven by dynamic markets and evolving consumer expectations, effective planning and execution are critical for achieving success. SOSTAC, a marketing planning model developed by PR Smith in the 1990s, provides businesses and individuals with a structured framework to enhance their planning and achieve their objectives. By breaking down the planning process into six actionable steps—Situation, Objectives, Strategy, Tactics, Action, and Control—SOSTAC ensures a comprehensive approach to decision-making. This white paper explores the intricacies of SOSTAC, its practical applications, and how it can be leveraged to improve planning and achieve sustainable growth.
The SOSTAC model has gained significant recognition due to its simplicity and adaptability. It transcends industries and organizational sizes, making it an invaluable tool for startups, established corporations, and individuals aiming to streamline their planning processes. The structured nature of SOSTAC not only facilitates clarity in setting objectives but also ensures that every action is aligned with the overarching strategy. This adaptability has allowed SOSTAC to become a cornerstone in the toolkit of modern marketers, business strategists, and planners.
One of the key strengths of the SOSTAC model lies in its ability to address complex challenges by breaking them down into manageable components. Each step—from Situation Analysis to Control—is designed to provide insights and direction that collectively contribute to the success of the overall plan. For example, the Situation Analysis phase allows businesses to critically assess their current position, enabling them to identify strengths to leverage and weaknesses to address. This foundational understanding ensures that subsequent steps are rooted in reality, rather than assumptions.
Understanding SOSTAC SOSTAC serves as an intuitive framework for planning that encompasses:
- Situation Analysis: Understanding where the business or individual currently stands. This step involves analyzing the internal and external environment to gain insights into strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT analysis).
- Objectives: Defining where the business wants to be. This involves setting SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) objectives aligned with the overall vision.
- Strategy: Determining the approach to achieve the objectives. Strategy defines the direction, including target audiences, value propositions, and competitive positioning.
- Tactics: Detailing how the strategy will be implemented. Tactics encompass specific actions such as marketing campaigns, communication channels, and resource allocation.
- Action: Translating tactics into an actionable plan. This step includes assigning responsibilities, establishing timelines, and ensuring effective execution.
- Control: Monitoring and measuring the performance against objectives. Control mechanisms involve setting KPIs (Key Performance Indicators), regular evaluations, and adjusting strategies based on results.
How SOSTAC Works The SOSTAC model operates as a cycle, beginning with situation analysis to identify the current state of affairs. Insights from this analysis shape strategic and tactical decisions. Strategies define the overarching approach, while tactics outline the finer details, such as communication and marketing mixes. Action plans operationalize these tactics, ensuring alignment with the objectives. Control measures provide a feedback loop to refine the process and drive continuous improvement.
Applications of SOSTAC SOSTAC’s versatility makes it applicable across various domains, from business planning to personal goal-setting. Below are its primary applications:
1. Marketing Strategies and Campaigns
- Situation Analysis: Conduct market research and competitor analysis.
- Objectives: Set goals such as increasing market share, improving brand awareness, or boosting sales.
- Strategy: Define target audiences and positioning.
- Tactics: Choose the appropriate marketing mix (e.g., product, price, place, promotion).
- Action: Launch campaigns with defined roles and timelines.
- Control: Track performance using analytics and adjust campaigns based on real-time data.
2. Business Planning
- SOSTAC can guide overall business strategy, from launching new products to entering new markets.
- Integrating tools like SWOT analysis, PESTEL analysis, and customer journey mapping can enrich the situation analysis.
3. Personal Development
- Individuals can use SOSTAC to plan personal goals, such as career growth or skill acquisition.
- Define clear objectives, devise a strategic approach, and implement actionable steps while monitoring progress.
Benefits of SOSTAC The model’s benefits go beyond its structured approach, offering key advantages such as:
- Clarity and Focus: By breaking the planning process into six distinct steps, SOSTAC ensures that businesses and individuals maintain clarity at every stage of their journey.
- Flexibility and Scalability: The model can be applied to projects of any size, from small-scale personal goals to large organizational strategies.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: SOSTAC promotes data-driven decisions by emphasizing thorough situation analysis and measurable objectives.
- Accountability: The Action and Control steps ensure that responsibilities are assigned, progress is monitored, and adjustments are made as needed.
- Continuous Improvement: The cyclical nature of SOSTAC allows for ongoing refinement of strategies and tactics based on feedback and results.
Challenges in Implementing SOSTAC While SOSTAC is a robust framework, its effectiveness depends on:
- Comprehensive Situation Analysis: Overlooking key factors during this step can lead to flawed strategies and missed opportunities.
- Alignment Across Teams: Effective implementation requires seamless collaboration between departments or stakeholders.
- Adaptation to Dynamic Markets: Strategies and tactics must remain agile to respond to market changes or emerging trends.
- Effective Measurement: Defining relevant KPIs and ensuring access to accurate data are essential for evaluating success.
Case Studies: SOSTAC in Action
Case Study 1: Small Business Growth
A local retail business used SOSTAC to increase its online presence and sales:
Situation: Limited online presence and declining foot traffic.
Objectives: Achieve a 20% increase in online sales within six months.
Strategy: Focus on local SEO and targeted social media ads.
Tactics: Optimize website for local search, create engaging social media content, and run promotions.
Action: Assign roles for content creation, ad management, and analytics tracking.
Control: Monitor web traffic, ad performance, and sales data.
Case Study 2: Personal Career Advancement
An individual applied SOSTAC to achieve career growth:
Situation: Stagnant role with limited responsibilities.
Objectives: Secure a managerial position within one year.
Strategy: Build skills and expand professional network.
Tactics: Enroll in leadership courses, attend networking events, and update LinkedIn profile.
Action: Allocate weekly time for skill-building and outreach.
Control: Track job applications, interview invitations, and skill development milestones.
Case Study 3: Launching a New Product
A startup developed a unique eco-friendly water bottle but lacked market awareness.
Situation: A startup developed a unique eco-friendly water bottle but lacked market awareness.
Objectives: Achieve $50,000 in sales within the first quarter post-launch.
Strategy: Target environmentally conscious consumers via digital platforms.
Tactics: Run influencer campaigns, create educational content, and partner with eco-focused retailers.
Action: Assign teams for content creation, influencer outreach, and retailer collaboration.
Control: Track website traffic, conversion rates, and retailer feedback.
Case Study 4: Community Event Promotion
A city council wanted to boost attendance at a local arts festival.
Situation: A city council wanted to boost attendance at a local arts festival.
Objectives: Increase attendance by 30% compared to the previous year.
Strategy: Leverage social media and community partnerships for outreach.
Tactics: Develop a social media calendar, collaborate with local influencers, and distribute flyers.
Action: Delegate roles for content posting, sponsorship coordination, and on-ground promotion.
Control: Analyze ticket sales, social media engagement, and attendance data.
Case Study 5: Nonprofit Fundraising Campaign
A nonprofit struggled to meet its annual fundraising goal.
Situation: A nonprofit struggled to meet its annual fundraising goal.
Objectives: Raise $100,000 within three months.
Strategy: Appeal to past donors and expand reach through digital platforms.
Tactics: Launch email campaigns, organize virtual events, and use storytelling videos.
Action: Assign tasks for donor outreach, content creation, and event planning.
Control: Track donations, campaign engagement, and event attendance.
Case Study 6: E-Learning Platform Expansion
An e-learning platform had plateaued in user acquisition.
Situation: An e-learning platform had plateaued in user acquisition.
Objectives: Increase user registrations by 25% within six months.
Strategy: Target young professionals and students through online advertising.
Tactics: Offer free trials, partner with universities, and run targeted LinkedIn ads.
Action: Dedicate resources to ad management, partnership building, and trial user engagement.
Control: Monitor registration metrics, ad performance, and user feedback.
Case Study 7: Fitness Studio Recovery Post-Pandemic
A fitness studio faced reduced memberships post-COVID-19.
Situation: A fitness studio faced reduced memberships post-COVID-19.
Objectives: Recover 50% of pre-pandemic memberships within four months.
Strategy: Rebuild trust and incentivize returns through hybrid fitness offerings.
Tactics: Offer discounted packages, promote safety protocols, and introduce virtual classes.
Action: Design promotional campaigns and re-train staff for hybrid operations.
Control: Track membership sign-ups, class attendance, and customer reviews.
Case Study 8: Sustainable Business Transformation
A mid-sized company aimed to reduce its carbon footprint.
Situation: A mid-sized company aimed to reduce its carbon footprint.
Objectives: Cut carbon emissions by 20% within one year.
Strategy: Implement sustainable practices across operations.
Tactics: Optimize supply chain, reduce energy usage, and launch green initiatives.
Action: Assign teams to audit current practices and execute green projects.
Control: Track energy savings, supplier changes, and emissions data.
Case Study 9: Personal Health Improvement Plan
An individual wanted to improve overall health and fitness.
Situation: An individual wanted to improve overall health and fitness.
Objectives: Lose 10 pounds and improve endurance within three months.
Strategy: Focus on balanced nutrition and consistent exercise.
Tactics: Follow a meal plan, join a fitness class, and track progress using apps.
Action: Schedule workouts and prepare meals weekly.
Control: Monitor weight, fitness levels, and nutritional intake.
Case Study 10: Restaurant Brand Repositioning
A family-owned restaurant struggled with outdated branding.
Situation: A family-owned restaurant struggled with outdated branding.
Objectives: Attract a younger demographic and increase foot traffic by 20%.
Strategy: Revamp the brand with a modern, social-media-friendly image.
Tactics: Redesign the logo, update the menu, and create Instagram-worthy content.
Action: Hire designers, launch a rebranding campaign, and train staff on social engagement.
Control: Analyze foot traffic, social media engagement, and customer feedback.
Best Practices for Using SOSTAC
- Integrate Complementary Tools: Combine SOSTAC with SWOT, PESTEL, and customer journey mapping for a more robust analysis.
- Embrace Agility: Continuously monitor performance and be prepared to adapt strategies based on insights.
- Focus on Metrics: Establish clear KPIs to measure progress effectively.
- Engage Stakeholders: Ensure alignment and collaboration across teams to drive successful implementation.
- Document and Communicate Plans: Maintain transparency and clarity by documenting each phase of SOSTAC.
Furthermore, the emphasis on measurable objectives and control mechanisms ensures that progress is not only monitored but also optimized. By integrating data-driven insights, SOSTAC helps organizations and individuals make informed decisions, adapt to changes, and stay ahead in competitive environments. Its cyclical nature fosters a culture of continuous improvement, making it a dynamic framework that evolves alongside market trends and organizational growth.
In the following sections, we delve deeper into each component of SOSTAC, illustrating how businesses and individuals can harness its principles to achieve their goals. We also explore best practices, challenges, and real-world applications, demonstrating the model’s relevance in various contexts. Through this exploration, readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of SOSTAC and its potential to transform planning and execution in today’s fast-paced world.
The foundational strength of SOSTAC lies in its adaptability and structured approach to planning. In today’s global economy, where change is the only constant, having a framework that can adapt to diverse challenges and industries is indispensable. SOSTAC provides a roadmap not only for marketing but also for other domains such as business development, project management, and even personal growth. By addressing each step with precision, this model ensures that no aspect of planning is overlooked, making it an essential tool for success.
At its core, the Situation Analysis phase sets the stage for success. It is during this stage that businesses and individuals examine their current position, identifying internal and external factors that impact their objectives. This analysis often includes tools such as SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) and PESTEL (Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, Legal) frameworks to gain a comprehensive understanding of the environment. These insights are critical for crafting strategies that are not only innovative but also grounded in reality.
For individuals, the Situation Analysis step can be particularly enlightening. For example, a professional looking to advance their career might conduct a personal SWOT analysis, identifying their unique strengths, areas for improvement, opportunities for growth, and potential challenges. This process provides clarity and focus, enabling them to set realistic and achievable goals. Similarly, small businesses aiming to expand their market share can use this phase to evaluate competitors, customer preferences, and industry trends, ensuring that their strategies are aligned with market demands.
Beyond analysis, the Objectives phase plays a crucial role in defining success. Objectives act as the guiding light, ensuring that every strategy and tactic is purpose-driven. By adhering to the SMART criteria, businesses and individuals can create objectives that are not only clear but also actionable. For instance, a company aiming to increase its digital presence might set an objective to grow website traffic by 30% within six months. This specificity ensures that all subsequent actions are focused and measurable, enhancing the likelihood of success.
In essence, the Situation Analysis and Objectives phases form the bedrock of the SOSTAC model. By investing time and effort in these initial steps, businesses and individuals can lay a strong foundation for strategic planning. As we continue to explore the nuances of SOSTAC, we will uncover how each subsequent step builds on this foundation, driving effective execution and measurable results.
Strategy serves as the bridge between understanding the current situation and executing actionable tactics. It is a critical phase of the SOSTAC model that defines the “how” in achieving objectives. By establishing a clear direction and prioritizing resources, a well-crafted strategy ensures that every subsequent step aligns with the organization’s vision and goals. For businesses and individuals alike, the Strategy phase is where creativity meets practicality.
The hallmark of an effective strategy is its focus on positioning. This involves identifying the target audience and crafting a unique value proposition that resonates with them. For instance, a tech startup aiming to disrupt the wearable fitness market may position itself as a provider of highly personalized health insights. This positioning not only differentiates the company but also forms the foundation for its marketing and operational tactics.
For individuals, strategy development might include career advancement plans or personal branding initiatives. Consider a freelance graphic designer seeking to attract premium clients. Their strategy might focus on showcasing expertise through a niche portfolio, leveraging social media platforms, and networking within industry-specific events. This clarity of direction ensures that all efforts contribute to achieving their professional objectives.
A robust strategy also anticipates potential challenges and outlines contingency plans. This proactive approach enables businesses and individuals to navigate uncertainties without derailing their progress. For example, a retail brand entering a new market might identify potential risks such as cultural differences or regulatory barriers. By addressing these risks within their strategy, they can mitigate potential setbacks and seize opportunities with confidence.
Moreover, aligning strategy with broader organizational or personal values enhances long-term success. Businesses that prioritize sustainability, for instance, can integrate eco-friendly practices into their strategy, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers. Similarly, individuals aligning their goals with core values find greater fulfillment and consistency in their pursuits.
In conclusion, the Strategy phase of SOSTAC is where vision transforms into actionable plans. It sets the stage for the Tactics phase, ensuring that every action is purposeful and aligned with the overarching goals. By investing in thoughtful strategy development, businesses and individuals can build resilient, adaptable plans that drive success in dynamic environments.
The Tactics phase in the SOSTAC model focuses on the finer details of how a strategy will be executed. This step transforms the high-level strategic direction into specific, actionable initiatives, ensuring alignment with the overall objectives. Tactics serve as the building blocks of a plan, dictating the day-to-day activities that bring the strategy to life. By emphasizing meticulous planning and precise execution, this phase bridges the gap between conceptual frameworks and tangible outcomes.
One of the most impactful aspects of the Tactics phase is its emphasis on the marketing mix, which includes product, price, place, and promotion. Each element is scrutinized to ensure optimal alignment with the target audience and the market environment. For instance, an e-commerce company aiming to increase customer retention might focus on personalized email campaigns, exclusive discount programs, and a user-friendly website interface as core tactics. These initiatives directly address customer preferences and enhance brand loyalty.
Tactics also extend beyond marketing to encompass operational efficiency and resource allocation. For example, a logistics firm entering a new market might develop tactical plans to streamline supply chain processes, reduce transit times, and improve last-mile delivery. These granular actions ensure that the firm’s strategic goals, such as penetrating the market and delivering exceptional customer service, are achieved effectively.
Individuals, too, can benefit from detailed tactical planning. A job seeker with a strategic objective to secure a management position within six months might implement tactics such as networking on LinkedIn, attending industry-specific seminars, and tailoring their resume for each application. These actions provide a clear roadmap, transforming aspirations into achievable milestones.
The Tactics phase also highlights the importance of integrating digital tools and platforms to optimize results. In today’s digital-first world, leveraging technologies such as customer relationship management (CRM) systems, analytics dashboards, and social media automation can significantly enhance the effectiveness of tactical execution. These tools provide real-time insights and streamline workflows, enabling businesses and individuals to adapt swiftly to changing circumstances.
Ultimately, the success of the Tactics phase depends on clarity, consistency, and coordination. Each action must serve a specific purpose, contributing to the overall strategy while addressing immediate objectives. In the next phase—Action—these carefully designed tactics are operationalized, translating plans into measurable outcomes that drive progress and ensure accountability.
The Action phase of the SOSTAC model is where plans are set in motion. It translates the well-crafted strategies and tactics into operational reality, ensuring that every task is executed with precision and purpose. While strategy and tactics provide the blueprint, the Action phase represents the execution stage, demanding effective coordination, resource management, and clear communication across all involved parties.
One critical aspect of the Action phase is defining roles and responsibilities. Clear accountability ensures that each team member or stakeholder understands their contribution to the overarching objectives. For example, a product launch campaign might involve marketing teams handling promotional content, sales teams preparing for increased demand, and customer service teams ready to address inquiries. Without clearly defined roles, even the best strategies can falter due to miscommunication or inefficiencies.
Another key component is the creation of a detailed timeline or project roadmap. This schedule should outline milestones, deadlines, and key performance indicators (KPIs) for tracking progress. For instance, a company planning to implement a new digital marketing strategy may break the timeline into phases—setting up analytics tools, creating content, launching campaigns, and measuring results. This phased approach ensures that the execution is structured and manageable, allowing for adjustments along the way.
Incorporating agility into the Action phase is crucial, particularly in dynamic environments. Flexibility enables organizations and individuals to respond to unforeseen challenges or capitalize on emerging opportunities. For example, a company launching a social media campaign may notice higher-than-expected engagement on a particular platform and shift resources to maximize impact. This adaptive mindset ensures that the plan remains relevant and effective throughout its execution.
Collaboration and communication are equally vital during this phase. Teams must work cohesively, sharing updates, insights, and feedback to stay aligned with the plan. Tools like project management software, regular check-ins, and collaborative platforms can facilitate seamless communication, ensuring that all stakeholders are informed and engaged.
For individuals, the Action phase might involve setting daily or weekly goals to maintain momentum toward personal or professional objectives. For example, an entrepreneur aiming to secure funding might schedule investor meetings, refine pitch decks, and conduct market research in parallel. These actions, guided by the strategy and tactics outlined earlier, build toward the ultimate goal.
In conclusion, the Action phase is the bridge between planning and results. By focusing on accountability, structured timelines, adaptability, and collaboration, businesses and individuals can ensure the successful implementation of their plans. The final phase of SOSTAC—Control—provides the mechanisms to evaluate these actions, measure success, and refine the approach for continuous improvement.
The final stage of the SOSTAC model, Control, ensures that all efforts are evaluated and optimized for maximum effectiveness. This phase revolves around monitoring, measuring, and analyzing outcomes to determine whether the objectives have been met. By providing valuable feedback, the Control phase not only assesses success but also identifies areas for improvement, fostering a cycle of continuous learning and refinement.
At the heart of the Control phase is the use of key performance indicators (KPIs). These measurable metrics align directly with the objectives set during the planning phase. For example, a digital marketing campaign might use KPIs such as website traffic, conversion rates, and return on investment (ROI). By tracking these metrics, businesses can gain insights into the campaign’s performance and make data-driven decisions to enhance future initiatives.
In addition to KPIs, regular reporting is a critical component of the Control phase. Reports provide a structured way to present data, analyze trends, and highlight key findings. A retail business, for instance, might generate weekly sales reports to monitor progress toward revenue targets. These reports help identify patterns, such as seasonal fluctuations or shifts in customer behavior, enabling proactive adjustments to strategies and tactics.
Another essential element of the Control phase is benchmarking. Comparing performance against industry standards or competitors offers valuable context for evaluating success. For instance, a startup measuring its social media engagement might analyze how its metrics compare to similar businesses in the same niche. This approach helps set realistic expectations and identify opportunities for differentiation.
Control is not limited to retrospective analysis; it also encompasses predictive insights. Modern tools, such as machine learning algorithms and predictive analytics software, enable organizations to forecast trends and anticipate outcomes. These technologies empower businesses to stay ahead of the curve, making informed decisions that preempt challenges and seize opportunities.
For individuals, the Control phase is equally transformative. A professional pursuing career advancement might evaluate their progress by tracking milestones, such as skill acquisition, professional certifications, or network growth. Regular self-assessment fosters accountability and ensures that efforts remain aligned with long-term goals.
Finally, the iterative nature of the Control phase reinforces the adaptability of the SOSTAC model. Insights gained during this stage feed directly into future planning cycles, creating a feedback loop that drives continuous improvement. For example, a company that identifies underperforming advertising channels can redirect resources to more effective platforms in subsequent campaigns.
In conclusion, the Control phase is the keystone of the SOSTAC model, ensuring that every effort is measured, evaluated, and optimized. By integrating robust monitoring tools, clear KPIs, and a commitment to continuous learning, businesses and individuals can unlock the full potential of their plans, achieving sustainable success in an ever-evolving environment.
Conclusion SOSTAC is more than a planning model—it is a strategic enabler that drives clarity, focus, and measurable success. Businesses and individuals who adopt SOSTAC can navigate complexities, adapt to change, and achieve their objectives with precision. By systematically applying the model’s six steps and integrating complementary tools, stakeholders can unlock their full potential and foster sustainable growth. Whether planning a marketing campaign, business strategy, or personal development journey, SOSTAC offers a proven roadmap to success.
By understanding the intricacies of SOSTAC and embracing its structured yet flexible framework, businesses and individuals can transform their planning and execution processes to achieve greater success and sustainability in a competitive world.